What is the Kimberly Process?
- The Kimberly Process is an international initiative aimed at breaking the link between legitimate trade in diamonds and conflict diamonds.
- Conflict diamonds are rough diamonds used by rebel movements or their allies to finance conflict aimed at undermining legitimate governments.
- The Kimberly Process (KP) represents a unique United Nations mandated joint initiative by approximately 75 countries, the international diamond industry and civil society to stop the flow of conflict diamonds. It imposes extensive legally binding requirements on participants to certify that rough diamonds (both exported and imported) are conflict free.
- It was launched in May 2000 in Kimberly, South Africa. The Kimberly Process Certification Scheme (KPCS) was adopted at a Ministerial Meeting in Interlaken, Switzerland in November 2002 and implementation began on 1st January 2003.
Why is it needed?
- Consumer awareness endangered the diamond industry, thereby jeopardizing the many countries which rely heavily on the diamond trade.
- The trade in polished diamonds will be more transparent and secure, thereby giving consumers the confidence that the diamonds they buy are clean.
- The KPCS also provides a greater regulatory framework for the diamond industry, something which gives the industry credibility.
- It provides a platform for countries to promote conflict-free diamonds e.g. Botswana’s Diamond for Development campaign.
- The World Diamond Council governs the process and is made up of State representatives, non-government organizations, and diamond companies.
How does the Kimberly Process work?
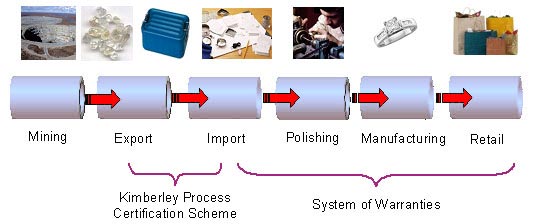
What is the ‘System of Warranties’?
- This requires that every time diamonds (rough, polished or in Jewellery) change hands the seller must affirm on the invoice that the diamonds have been purchased through official channels and therefore not involved in conflict funding.
- All members of the trade who provide such assurances have promised to keep records of their diamonds’ clean roots (and therefore their clean path to the market). Those records will be monitored by companies’ individual auditors as part of their regular duties.
- The appropriate government authorities may request to see the report on warranties issued and received.
- All DTC clients subscribe to Diamond Best Practice Principles (BPPs). BPPs stipulate that all clients must adhere to the KP; furthermore, 10% of all clients are audited annually to ensure that such standards are met.
What Does the Kimberly Process Require of the Trade?
Mining companies and rough diamond buyers:
- Must keep able records to demonstrate that diamonds were mined or purchased from legitimate source and conflict free source.
- Need to provide a System of Warranties declaration to accompany all transactions within the country.
Recipients of rough Diamonds:
- Must be a KP participant country and shipment must come from a KP participant country
- If a shipment crosses a national border it must be accompanied by the System of Warranties declaration
- Recipients must keep records of KP certificates and warranties for auditing
NB: To re-export, recipients must apply for Re-export Certificate and show that all previous transactions were accompanied by a System of Warranties declaration.
Diamond polishers, manufacturers, dealers and retailers:
- Polished diamonds do NOT need a KP Certificate for export however, each sale of polished diamonds requires an industry System of Warranties declaration
- Must keep records of warranties for auditing by own accountants
It is the responsibility of all members of the trade to:
- Act decisively to ensure that never again can conflict diamonds enter the legitimate trade
- Understand the issues surrounding Conflict diamonds.
